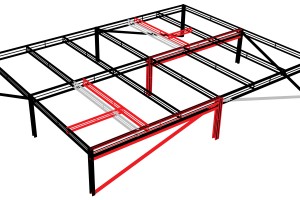
Traditional construction methods such as stick-framing cold-formed steel (CFS) walls have been in use for a long time. Stick framing involves wastage of material and requires skilled field labor, slower build time, and scheduling around favorable weather. With advancements in technology, we are now witnessing the early stages of innovation in the architecture, engineering, and construction (A/E/C) industry using automation.
…Review Category : Technology
Changing the Way Engineers Work
Engineers are constantly trying to find new ways to optimize processes to perform their duties more effectively. Implementing drone or Unmanned Arial Vehicle (UAV) technology in their projects is one solution engineers have found over the past few years and are starting to use.
…Humans have been building with biology for thousands of years. Dimensional lumber and mass timber are mature technologies based on materials produced using biological processes. Today, there is fertile ground for additional research and development of materials based on biological processes or biomimetic principles finding application in structural engineering. Advancements in biotechnology are giving rise to new biomaterials for construction that go beyond wood; bioinspired structures and biomimicry are potential tools to augment existing and entirely new structures. The term biomimicry is derived from the words bios and mimicry coming from the Greek language meaning life and imitation, respectively. The fundamental tenet of biomimicry is to mimic nature and leverage the biological principles that have resulted from evolutionary processes.
…Applying Computational Design Logic to the Quality Control Process
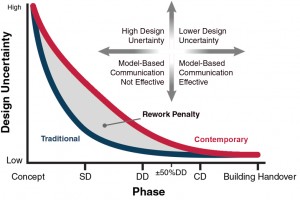
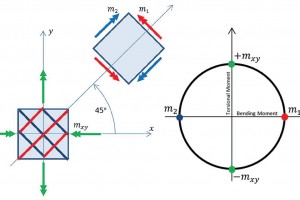
The future of structural engineering is inextricably linked with computational design. Algorithms and data will be the basis upon which the industry develops. That is not to say that engineering judgment and expertise will be replaced by artificial intelligence. Instead, the possibilities of computer programming will continue to enhance the capabilities of structural engineers just as the widespread adoption of the computer did in the 1980s. Some engineers in the industry have been working in the field of computational design for over a decade. Others have been slower to adapt.
…Why Now and How Do You Use It?
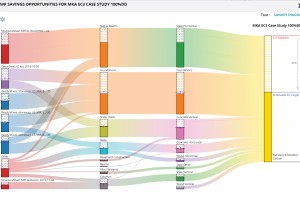
The building and construction sectors play a vital role in minimizing our future carbon footprint. Each year, the built environment contributes almost 40% of global greenhouse (GHG) emissions. The industry’s focus on operational carbon reductions – the energy used to heat, cool, and power our buildings – has led to many successes. However, the attention to embodied carbon, the emissions associated with material production and construction processes, has been lagging. …
Assistance for Building Façade Assessment
Building owners need to routinely assess the condition of their building façades for many reasons, including compliance with façade inspection ordinances, to check for deterioration, to monitor known deterioration, and to plan for maintenance and capital repairs. Traditional methods for façade inspection include ground-based visual observations and hands-on inspection using various means of access, which both have limitations. Access to building façades for hands-on inspection can range from straightforward to very complex. The more complexity involved in accessing the façade, the higher the costs, and the less likely that building owners will routinely assess the conditions of their building façades, potentially allowing deterioration to occur unchecked. …
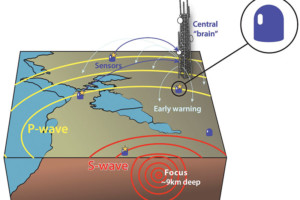
How Earthquake Early Warning Systems Can Aid Recovery Efforts
Buildings and residents near the Salton Sea began shimmying and shaking during the swarm of earthquakes that burst from Bombay Beach in late September 2016. Soon, the California Earthquake Prediction Evaluation Council (CEPEC) released a statement. It read: “CEPEC believes that stresses associated with this earthquake swarm may increase the probability of a major earthquake on the San Andreas Fault to values between 0.03 percent and 1.0 percent for an M7.0 or larger earthquake occurring over the next week (to 09:00 hrs PDT, Tuesday, October 4, 2016).” …