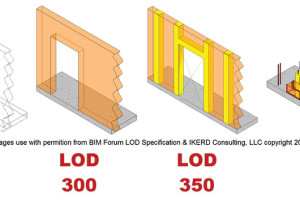
Clearly defined structural engineering contract scopes save engineers time, profit, and – most importantly – the personal satisfaction of their profession. Building Information Modeling (BIM) can improve this scope clarity if addressed proactively, or compound the difficulties in achieving clarity if ignored. The construction industry has reached a point where the use of BIM is not self-explanatory: it could be used to create 2D shop drawings, coordinate trades, or estimate cost. …
Review Category : InSights
What is it and Who is Responsible?
Many types of ground improvement (GI) are used in modern geotechnical construction. For the purpose of this article, GI refers to a rigid or semi-rigid cylindrical inclusion (GI element) installed through otherwise unsuitable bearing soils into underlying suitable strata to enable the use of spread footing foundations for building support. Due to favorable economics compared to viable foundation alternatives, use of GI is accelerating in the United States. …
Steel floor or roof deck is only as good as its fastening. Whether it is the performance of the product as a diaphragm to transfer wind or seismic forces, resisting wind uplift, acting as a concrete form, providing bracing to beams or joists, or providing a safe working platform during construction, proper fastening makes the deck do its job. …
The Future of Concrete Durability
In a building landscape where the expected lifespan of a structure is longer than usual, the durability of the materials that encompass the structure become more critical. Sustainability is key for any structures viability in today’s construction world, which means new technologies are of great value to not only the project teams, but also the environment. …
How much more efficient would structural engineers be if they had access to all of their resources wherever they want? Imagine if resources like construction documents, as-built drawings, project correspondence, calculations, building codes, reference materials, computer analysis programs, product manuals, colleagues, etc. could be carried to every meeting, hauled around to every jobsite and brought home every night. …
In construction, time is money. And, when it comes to saving time and increasing productivity, the cloud is a catalyst for change. Arguably one of the most game-changing technologies of the century, the cloud to the computer industry is like utility grids for the power industry – a central fabric that powers the most complex computing tasks. However, it may be the simple things that result in the greatest business impact. Take, as an example, the access and sharing of important business documents and files. …
Coated reinforcing steel is widely used to provide corrosion protection to reinforced concrete against the effects of deicing and marine salts and carbonation. In North America, approximately 10 percent of all reinforcing is coated. Coated reinforcing steel utilizes the existing reinforcing bar stock and is available in sizes from 0.375 to 2.25 inches and in strengths from 40 to 80 ksi. …
What makes a bridge (or any other structure) sustainable? The American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE) defines sustainability as, “A set of environmental, economic and social conditions in which all of society has the capacity and opportunity to maintain and improve its quality of life indefinitely without degrading the quantity, quality or availability of natural, economic, and social resources.” …
Steel plate shear wall (SPSW) technology is advancing, making more wide-spread implementation of seismic force resisting systems possible. These stiff and ductile systems have had years of research that has demonstrated their excellent seismic performance, explored various details and configurations, and resulted in the design provisions in ANSI/AISC 341-10, where they are denoted special plate shear walls. The key principal for design is that yielding is expected in the web plates, at the beams ends and at the column bases. …
The Present State of the Industry
Formal concrete anchorage design provisions first appeared in ACI 318-02 as Appendix D, with applications limited to cast-in-place anchors and post-installed mechanical expansion anchors. …