Forensic structural engineering involves the investigation and determination of the causes of a failure of structures such as bridges, buildings, industrial structures, and metro stations. (Figure 1). Along with understanding the legal procedures and giving testimony, forensic structural engineers use their knowledge and experiences in these investigations to act as a detective, investigator, and expert witness when confronted by attorneys and other opposing experts during the litigation process.
…Review Category : Guest Column
As a result of the global pandemic, construction materials such as steel – a necessary material for use in traditional concrete applications – have been impacted by price increases and material shortages. Although this may be concerning for businesses and municipalities undertaking construction projects involving parking decks, roads, bridges, and other concrete-related repairs, it may open up the opportunity to utilize the short-term and long-term benefits of fiber-reinforced concrete.
…System Description
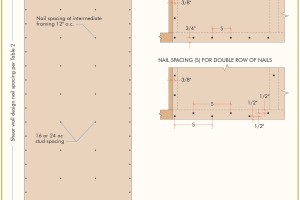
Using wood structural panels that are required to resist lateral loads and normal wind load requirements of the IBC Section 1609.6.4.4.1, Chapter 30 of ASCE-7, or IRC Section R301.2.1, additional wind uplift resistance from the panel can be achieved by providing additional nails to the shear nailing at the top and bottom of the panel. These additional nails are used to transfer the uplift forces from the top plate to the panel, from panel to panel at splice locations (if present), and from panel to sill plate at the foundation, effectively eliminating the need for uplift straps at these locations. Uplift straps may still be required around window and door openings in exterior walls to transfer the wind uplift loads acting on the header to the foundation below.
…Effect of Large Diameter Horizontal Holes
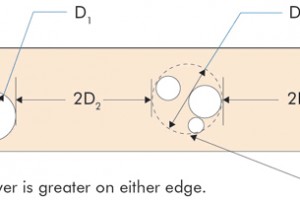
Structural glued laminated timber (glulam) beams are highly engineered components manufactured from specially selected and positioned lumber laminations of varying strength and stiffness. As most glulam beams are designed for and used in applications where they are highly stressed under design loads, drilling or notching of glulam should be avoided and never done without a thorough understanding of the effects on the structural integrity of a member. This is specifically addressed in Section R502.8.2 of the 2021 International Residential Code (IRC) as follows (the same wording also appears in Section R802.7.2 of the 2021 IRC):
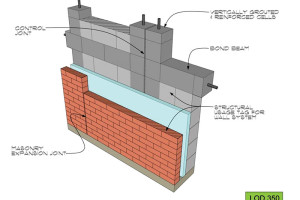
…The phrase “the devil is in the details” applies to anchor bolt design in masonry structures. The anchorage of masonry members is essential both for load transfer into the member and for stability and support of the member. There are typically two types of anchors used in masonry. Cast-in-place anchors, or anchor bolts, are generally designed using TMS 402 Building Code Requirements for Masonry Structures. Post-installed anchors are generally designed based on manufacturers’ data, with the design capacities of the anchors determined through International Code Council (ICC) Evaluation Service reports. This article focuses on anchor bolt design and, particularly, several recent revisions in the 2016 version of TMS 402 that will help with the design of anchor bolts.
…The REACH, a 72,000-square-foot expansion of the John F. Kennedy Center for the Performing Arts in Washington, DC, received the Overall Excellence Award in the 2020 American Concrete Institute’s (ACI) Excellence in Concrete Construction Awards program. The REACH is comprised of three prominent pavilions connected by studios, classrooms, and a parking structure below an interwoven green roof. This article provides insights into the execution of some of the project’s outstanding features.
…A Guide to Selection and Specification
Cross-laminated timber (CLT) is a prefabricated, solid engineered mass timber panel. Because CLT is prefabricated, most components arrive ready to assemble and go together very quickly. CLT’s large-scale components enable faster construction, not only because of prefabrication but because fewer joints are needed between elements.
…Cast-in-Place Concrete Edge Barrier Walls in Parking Structures
The April 2014 issue of STRUCTURE magazine featured an article in the Structural Failures column, titled Design Deficiencies in Edge Barrier Walls in Parking Structures, by Mohammad Iqbal, D.Sc., P.E., S.E., Esq. The article brought up important points related to the adequacy of upturned cast-in-place (CIP) concrete barrier walls supported on slab edges to withstand code-prescribed vehicle barrier loads in parking structures. …
To unify the masonry industry and all supporting industries through the development and implementation of BIM for masonry software to facilitate smoother workflows and collaboration across all disciplines from owner, architect, engineer, manufacturer, mason, contractor, construction manager, and maintenance professionals. …
Of course, many of the same principles still apply…outstanding corrosion protection, metallurgical bonding,100% surface protection of the interior and exterior of steel fabrications… but the galvanizing industry has adapted to the demands of the 21st century by recognizing that there is more to it than stopping rust. This article will highlight some of the technical and marketing trends benefitting the engineering community. …